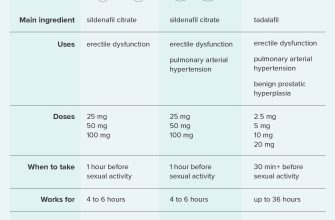
Need clear information about Atorvastatin 5mg tablets? Start with dosage: always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Never adjust your dosage without consulting them. Incorrect usage can negatively impact treatment efficacy.
This medication helps lower cholesterol. Atorvastatin belongs to a class of drugs called statins. They work by blocking a substance your liver needs to produce cholesterol. Regular use contributes to improved cardiovascular health by reducing LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and triglycerides.
Potential side effects include muscle aches, nausea, and constipation. While generally well-tolerated, promptly report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. They can assess your situation and adjust treatment if necessary. Remember that individual responses to medication vary.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist before starting any new medication, including Atorvastatin. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health needs and medical history. Never disregard or delay seeking medical advice due to information found online.
- Atorvastatin 5 mg Tablet: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Atorvastatin 5mg
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- What is Atorvastatin 5 mg?
- Mechanism of Action: How Atorvastatin Lowers Cholesterol
- Indications for Use: When is Atorvastatin 5 mg Prescribed?
- Specific Conditions Treated with Atorvastatin 5 mg
- Dosage and Administration: How to Take Atorvastatin 5 mg
- Potential Side Effects: What to Watch Out For
- Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid While Taking Atorvastatin
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Other Medications Requiring Caution
- Warfarin
- Always Inform Your Doctor
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- Precautions and Warnings: Who Should Not Take Atorvastatin
- Monitoring Your Progress: What to Expect During Treatment
- Blood Test Results & Dosage Adjustments
- Monitoring Side Effects
- Alternatives and Lifestyle Changes: Beyond Medication
Atorvastatin 5 mg Tablet: A Detailed Guide
Take Atorvastatin 5mg exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Don’t adjust your dosage without consulting them.
Understanding Atorvastatin 5mg
This medication lowers cholesterol levels in your blood. It’s a statin, working by blocking a substance your liver needs to produce cholesterol. Lower cholesterol reduces your risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Dosage: Your doctor determines the appropriate dose based on your individual needs and health status. 5mg is a common starting dose.
- Administration: Typically taken once daily, usually in the evening. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding timing.
- Food Interaction: Atorvastatin can be taken with or without food.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, Atorvastatin can cause side effects. While many experience no problems, some may experience:
- Muscle aches (myalgia)
- Headache
- Stomach upset
- Nausea
Rare, but serious, side effects include liver damage and muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis). Report any unusual muscle pain, weakness, or dark urine to your doctor immediately.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Atorvastatin is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Discuss alternative options with your doctor.
- Drug Interactions: Certain medications can interact with Atorvastatin. Inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of liver damage. Moderation is advised while taking Atorvastatin.
Regular blood tests are often recommended to monitor your cholesterol levels and liver function while on Atorvastatin. This allows your doctor to adjust your dosage or monitor for potential issues.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized recommendations.
What is Atorvastatin 5 mg?
Atorvastatin 5 mg is a low-dose statin medication used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. It’s prescribed to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, particularly for individuals with high cholesterol or a family history of heart problems.
This low dose is often a starting point for treatment, allowing doctors to carefully monitor your response and adjust the dosage as needed. Higher doses are available if necessary. Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and frequency.
Atorvastatin works by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver responsible for cholesterol production. By reducing cholesterol production, your body can process and eliminate existing cholesterol more effectively. This lowers both LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and triglycerides, while potentially slightly increasing HDL (“good”) cholesterol.
| Common Side Effects | Possible Actions |
|---|---|
| Muscle aches (myalgia) | Report to your doctor; they might adjust the dosage or suggest alternative treatment. |
| Headache | Over-the-counter pain relief may help. Consult your doctor if persistent. |
| Digestive upset (e.g., nausea, constipation) | Consider taking the medication with food. Consult your doctor if severe or persistent. |
Before starting Atorvastatin 5 mg, inform your doctor about any pre-existing medical conditions, current medications, and allergies. Regular blood tests will monitor your cholesterol levels and the medication’s effects. Consistent adherence to your prescribed treatment plan, including lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise, is crucial for optimal results.
Mechanism of Action: How Atorvastatin Lowers Cholesterol
Atorvastatin works by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, a key enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. This enzyme is responsible for converting HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early precursor to cholesterol. By blocking this enzyme, atorvastatin reduces the liver’s production of cholesterol.
This reduction in cholesterol synthesis triggers a compensatory mechanism. The liver increases the number of LDL receptors on its surface. These receptors bind to and remove LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) from the bloodstream. This results in lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Simultaneously, atorvastatin also modestly increases HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol) levels and reduces triglyceride levels, further improving the lipid profile.
The net effect is a significant reduction in overall cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, contributing to a decreased risk of cardiovascular events.
Indications for Use: When is Atorvastatin 5 mg Prescribed?
Atorvastatin 5 mg is primarily prescribed to lower high cholesterol levels (hypercholesterolemia) and prevent cardiovascular disease. This low dose is often used for patients who need a gentler approach to cholesterol management or those with certain health conditions.
Specific Conditions Treated with Atorvastatin 5 mg
Doctors often prescribe this dosage for patients with: mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia, a family history of premature heart disease, type 2 diabetes with elevated cholesterol, a recent cardiovascular event (such as a heart attack or stroke), or other risk factors for cardiovascular disease like high blood pressure or smoking. It’s also used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.
This low dose may also be appropriate for individuals who experience muscle pain (myalgia) or other side effects at higher doses of statins. Remember that individual responses to atorvastatin vary, and your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your specific needs and health profile. Always discuss any concerns or side effects with your physician.
Dosage and Administration: How to Take Atorvastatin 5 mg
Take Atorvastatin 5 mg once daily, preferably in the evening with or without food. Consistency is key; try to take your medication at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels.
Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush, chew, or break the tablet. This ensures proper absorption.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate duration of treatment. Follow their prescribed regimen closely. Do not stop taking Atorvastatin without consulting your physician, even if you feel better.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses to make up for a missed one.
| Possible Side Effects | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Muscle aches, pain, or weakness | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation | These are generally mild and may subside. Contact your doctor if persistent or severe. |
| Rash, itching, swelling | Seek medical attention immediately. This may indicate an allergic reaction. |
Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, to avoid potential interactions.
Store Atorvastatin at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep it out of reach of children.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for any questions or concerns about your medication.
Potential Side Effects: What to Watch Out For
Atorvastatin, while generally well-tolerated, can cause some side effects. Most are mild and temporary, but knowing what to expect can help you manage them.
Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Muscle aches (myalgia)
- Stomach upset (nausea, constipation, diarrhea)
- Feeling tired or weak
- Skin rash
Less common, but more serious, side effects require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Muscle pain with weakness or tenderness (this could indicate rhabdomyolysis, a rare but serious condition)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored stools
- Allergic reactions such as swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Liver problems
Here’s what to do:
- Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Do not stop taking atorvastatin without first consulting your doctor.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and frequency.
- Consider keeping a record of your side effects and reporting them at your next appointment.
Remember, this information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice. Always discuss concerns with your doctor or pharmacist.
Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid While Taking Atorvastatin
Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice. These can significantly increase atorvastatin levels in your blood, potentially leading to side effects.
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Simultaneous use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, and ritonavir substantially raises atorvastatin blood levels. This heightened concentration increases the risk of myopathy, a potentially serious muscle disorder. Consult your doctor before combining atorvastatin with these medications.
Other Medications Requiring Caution
Certain medications may interact less severely but still warrant careful monitoring. These include cyclosporine, gemfibrozil, and other fibrates. Your doctor should adjust your atorvastatin dose or consider alternative therapies if necessary.
Warfarin
Combining atorvastatin with warfarin, a blood thinner, can increase your bleeding risk. Regular monitoring of your INR (international normalized ratio) is crucial during concurrent use.
Always Inform Your Doctor
Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting atorvastatin or adding any new medication to your regimen. This proactive approach helps prevent dangerous drug interactions and maximizes your safety.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Pay close attention to any unusual muscle pain, weakness, or tenderness. These could be signs of myopathy and require immediate medical attention.
Precautions and Warnings: Who Should Not Take Atorvastatin
Avoid atorvastatin if you have a history of allergic reactions to atorvastatin or any of its ingredients. This includes experiencing muscle aches, weakness, or pain (myalgia or rhabdomyolysis).
Women who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy should not take atorvastatin. The drug can harm the developing fetus or infant.
Individuals with liver disease, especially severe liver impairment, should consult their doctor before starting atorvastatin. Liver function tests may be needed to monitor for potential side effects.
Patients with a history of muscle disorders or a family history of muscle problems should exercise caution. Atorvastatin can, in rare cases, cause serious muscle damage.
Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice while taking atorvastatin. Grapefruit interacts with the medication and can increase its concentration in the bloodstream, potentially leading to increased side effects.
People taking certain medications, particularly other statins, some immunosuppressants, antifungals, and antibiotics, should discuss potential drug interactions with their physician before using atorvastatin.
Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new medication, including atorvastatin, to assess your individual risk factors and ensure its suitability.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any serious side effects.
Monitoring Your Progress: What to Expect During Treatment
Schedule regular checkups with your doctor. These appointments typically occur every 3-6 months, allowing for blood tests to monitor your cholesterol levels (LDL, HDL, triglycerides) and liver function. Your doctor will adjust your dosage as needed based on your results.
Blood Test Results & Dosage Adjustments
Expect your doctor to discuss your lipid profile results with you at each appointment. Lower LDL cholesterol is the primary goal. If your cholesterol levels aren’t improving sufficiently, your doctor might increase your Atorvastatin dosage. Conversely, if your levels are significantly reduced and side effects arise, they may decrease the dosage or consider alternative treatments.
Monitoring Side Effects
Report any muscle aches, pain, or weakness to your doctor immediately. These are potential side effects, and your doctor may need to adjust your medication or prescribe additional support. Pay attention to any unusual fatigue or digestive issues as well. Open communication is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Remember that consistent medication adherence is key. Take your Atorvastatin as prescribed, even if you feel well. Regular monitoring provides the best chance for managing your cholesterol and reducing long-term health risks.
Alternatives and Lifestyle Changes: Beyond Medication
Consider dietary adjustments. Reduce saturated and trans fats, focusing instead on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Aim for a Mediterranean-style diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon.
Increase physical activity. Target at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise weekly. Include strength training exercises twice a week.
- Examples of moderate-intensity activities: brisk walking, cycling, swimming.
- Examples of vigorous-intensity activities: running, jumping rope, high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Manage your weight. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve cholesterol levels. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized weight management strategies.
Quit smoking. Smoking significantly increases your risk of heart disease. Seek support from your doctor or utilize resources like nicotine replacement therapy to aid in quitting.
Reduce alcohol consumption. Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels. Men should have no more than two drinks per day, while women should have no more than one.
Manage stress. Chronic stress can negatively impact cholesterol levels. Explore stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Prioritize sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly.
- Monitor blood sugar: High blood sugar contributes to high cholesterol. Maintain healthy blood sugar levels through diet and exercise.
- Regular checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your cholesterol levels and overall health.
Remember, these lifestyle changes complement, not replace, medical advice. Always consult your doctor before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.