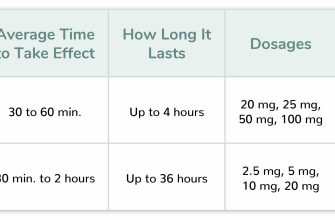
Considering Clomid? Start with understanding its primary use: boosting testosterone production in men with hypogonadism, a condition marked by insufficient testosterone. This isn’t a quick fix; results vary, and consistent monitoring is key. Expect potential side effects like headaches, hot flashes, and vision changes; your doctor will discuss these risks.
Clomid (clomiphene citrate) functions by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, triggering the release of more gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This, in turn, stimulates the production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), ultimately increasing testosterone levels. This process takes time; noticeable results might not appear for several weeks.
Dosage is crucial. Your physician will prescribe the correct amount based on your specific needs and medical history. Self-medicating is dangerous; always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Regular blood tests will monitor your testosterone levels and treatment progress, enabling timely adjustments.
Remember: Clomid isn’t a miracle drug. It may not be suitable for everyone. Factors like underlying health conditions, existing medications, and individual response significantly impact treatment success. Open communication with your doctor is paramount to ensure you receive the proper care and guidance. Discuss potential benefits and risks thoroughly before beginning treatment.
- Clomid Tablets for Men: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Clomid’s Role in Male Infertility
- Dosage and Treatment Duration
- Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Alternative Treatments and Considerations
- Success Rates and Expectations
- Lifestyle Changes to Support Treatment
- What is Clomid and How Does it Work in Men?
- Clomid’s Role in Treating Male Infertility: Indications and Effectiveness
- Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Clomid Use in Men
- More Serious Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration of Clomid for Men: A Doctor’s Guidance is Crucial
- Alternatives to Clomid for Male Infertility: Exploring Other Treatment Options
- Monitoring Progress and Long-Term Implications of Clomid Therapy
Clomid Tablets for Men: A Comprehensive Guide
Consult your doctor before using Clomid. It’s crucial for personalized assessment and monitoring.
Understanding Clomid’s Role in Male Infertility
Clomid (clomiphene citrate) primarily increases testosterone and sperm production in men with low levels. This medication affects the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, prompting them to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Increased FSH stimulates sperm production, while LH boosts testosterone.
Dosage and Treatment Duration
Your doctor determines the correct Clomid dosage, usually starting with 25mg daily for 3-6 weeks. Dosage adjustments depend on response and blood tests. Treatment duration varies; some men benefit from several cycles.
Potential Side Effects
Possible side effects include hot flashes, headaches, mood swings, and visual disturbances. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience severe or persistent symptoms. Rare but serious side effects require immediate medical attention.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular blood tests track hormone levels and sperm counts during and after treatment. These tests guide dosage adjustments and assess treatment success. Follow-up appointments are vital for ongoing monitoring and to address any concerns.
Alternative Treatments and Considerations
Clomid isn’t suitable for all men. Alternative treatments include other medications or assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress management positively impact fertility. Your physician will discuss all options.
Success Rates and Expectations
Clomid’s success rate varies depending on the cause of infertility and individual response. While it can significantly improve sperm parameters for some men, it doesn’t guarantee pregnancy. Realistic expectations and open communication with your doctor are key.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Treatment
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle enhances treatment response. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction contribute to better overall health and improve fertility chances. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
What is Clomid and How Does it Work in Men?
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is a medication primarily known for its use in women struggling with infertility. However, it also finds application in men experiencing low sperm counts or other fertility issues. It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that regulates hormone production. This blockage triggers the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
Increased FSH stimulates sperm production in the testicles, leading to a potentially higher sperm count. The rise in LH promotes testosterone production, which is also crucial for healthy sperm development and function. Therefore, Clomid’s action indirectly increases both sperm quantity and quality.
It’s important to understand that Clomid doesn’t work for everyone. Its efficacy varies depending on the underlying cause of male infertility. Some men might see significant improvements, while others may experience minimal or no effect.
| Potential Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Increased sperm count | Hot flashes |
| Improved sperm motility | Mood swings |
| Elevated testosterone levels | Visual disturbances |
| Increased chances of conception | Headaches |
Always consult a doctor before using Clomid. They can assess your individual situation, determine if Clomid is appropriate, and monitor your progress closely. Self-medicating with Clomid is strongly discouraged. Your physician will discuss potential risks and benefits and help you make an informed decision.
Clomid’s Role in Treating Male Infertility: Indications and Effectiveness
Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) helps some men with infertility by stimulating the pituitary gland to produce more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones are crucial for sperm production.
Clomid is primarily indicated for men with:
- Low sperm count (oligospermia)
- Low sperm motility (asthenospermia)
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (low FSH and LH levels)
However, it’s not a solution for all types of male infertility. Clomid’s success depends on the underlying cause of the infertility. For example, it won’t help if the problem stems from a blockage in the reproductive tract or genetic abnormalities.
Studies show varied success rates. Some research suggests pregnancy rates in couples using Clomid for male factor infertility range from 10-20%. This rate depends heavily on the specific diagnosis and the couple’s overall fertility profile. Factors like age and female partner’s fertility also influence outcomes.
Possible side effects include:
- Hot flashes
- Visual disturbances
- Headaches
- Nausea
Before starting Clomid treatment, a thorough evaluation by a reproductive endocrinologist or urologist is necessary. They’ll perform tests to pinpoint the exact cause of infertility and assess whether Clomid is appropriate. They will also monitor for side effects during treatment.
Remember: Clomid isn’t a guaranteed solution. A fertility specialist can explain the likelihood of success based on your specific situation and discuss alternative treatments if necessary.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Clomid Use in Men
Clomid, while effective for some men, carries potential side effects. These range from mild to severe, and their likelihood varies depending on dosage and individual factors. Common side effects include hot flashes, headaches, and visual disturbances like blurred vision or sensitivity to light. These usually resolve once treatment stops.
More Serious Side Effects
Less common but more serious side effects require immediate medical attention. Gynecomastia (breast enlargement) can occur, sometimes requiring surgery. Decreased sperm production can happen after treatment stops, though usually temporary. Liver damage is rare but a serious concern. Report any signs of liver problems, including jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes), dark urine, or unusual fatigue, to your doctor immediately. Changes in mood, including irritability or depression, are also reported. Finally, vision problems beyond temporary blurred vision, such as double vision or visual impairment, need swift medical review.
Always discuss potential risks with your doctor before starting Clomid. They will assess your individual health and weigh the potential benefits against the risks. Open communication is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Dosage and Administration of Clomid for Men: A Doctor’s Guidance is Crucial
Clomid dosage for men varies significantly depending on individual factors and the specific reason for prescription. A doctor will determine the appropriate starting dose, usually between 25 and 150 mg daily, for a specific period, often 5-8 weeks. This is not a self-prescribing medication; never adjust the dosage or duration without direct medical supervision.
The typical administration method involves taking the Clomid tablet orally, once daily, usually at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels. Your doctor will provide precise instructions tailored to your circumstances. Strictly adhering to your physician’s directions is critical for optimal results and to minimize potential side effects.
Monitoring is vital. Your doctor will schedule regular check-ups to assess your response to treatment and make adjustments if needed. This may involve blood tests to monitor hormone levels and sperm analysis to track the effectiveness of the medication. Reporting any side effects promptly is also paramount.
Common side effects include hot flashes, visual disturbances, headaches, and mood changes. These usually resolve once treatment stops. However, serious side effects, though rare, require immediate medical attention. Your doctor will discuss potential risks and benefits during your consultation.
Remember: Self-treating with Clomid is dangerous. Only a qualified healthcare professional can accurately diagnose infertility, prescribe the appropriate medication, and monitor your progress safely and effectively. They will personalize your treatment plan to optimize your chances of success while minimizing potential risks.
Alternatives to Clomid for Male Infertility: Exploring Other Treatment Options
If Clomid isn’t suitable or effective, several other treatments can boost male fertility. Let’s explore them.
- Lifestyle Changes: Optimizing your health is crucial. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and limiting alcohol and tobacco use. These simple changes often yield significant improvements.
- Hormone Therapy: Beyond Clomid, other medications like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) can stimulate testosterone production and sperm development. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate hormone therapy based on your specific needs and hormonal profile.
- Letrozole: This aromatase inhibitor can improve sperm parameters in some men by increasing testosterone levels. It’s an alternative for those who don’t respond well to Clomid.
For men with specific underlying conditions affecting fertility:
- Treatment of Varicoceles: A varicocele, an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, can impair sperm production. Surgical or minimally invasive procedures can correct this issue.
- Addressing Infections: Infections in the reproductive tract can negatively impact sperm quality and quantity. Treatment involves antibiotics to eradicate the infection.
- Treating Endocrine Disorders: Conditions like hypogonadism (low testosterone) may necessitate hormone replacement therapy to restore normal hormone levels and improve sperm production.
Advanced reproductive technologies are available when other treatments fail:
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is directly placed into the uterus to improve chances of fertilization.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved from the partner, fertilized with sperm in a laboratory, and the resulting embryos are transferred to the uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg to facilitate fertilization. This is particularly helpful for men with severe sperm issues.
Remember, consulting a fertility specialist is vital for a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan. They’ll conduct thorough tests to identify the root cause of infertility and recommend the most appropriate course of action.
Monitoring Progress and Long-Term Implications of Clomid Therapy
Regular semen analysis is key. Schedule these tests every 2-3 months to track sperm count, motility, and morphology improvements. Your doctor will guide you on the frequency based on your individual response.
Monitor your testosterone levels. Clomid can impact testosterone production; regular blood tests help ensure it remains within a healthy range. Discuss any unusual symptoms with your doctor immediately.
Be aware of potential side effects. These can include headaches, hot flashes, and vision changes. Report any persistent or worsening side effects promptly to your physician. They can adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments.
Long-term use of Clomid requires careful consideration. Extended therapy may increase the risk of liver damage and low sperm production once treatment stops. Your doctor will discuss the appropriate duration and potential long-term implications.
Consider lifestyle changes. Factors like diet, exercise, and stress management influence fertility. A healthy lifestyle can complement Clomid therapy and enhance its effectiveness.
Discuss alternative treatments. If Clomid proves ineffective, your doctor will explore other options such as hormone injections or assisted reproductive technologies. Open communication is vital for finding the best treatment plan.
Maintain regular communication with your physician. This ongoing dialogue ensures you receive appropriate monitoring and adjust treatment as needed. Your doctor’s expertise will guide you through your journey.