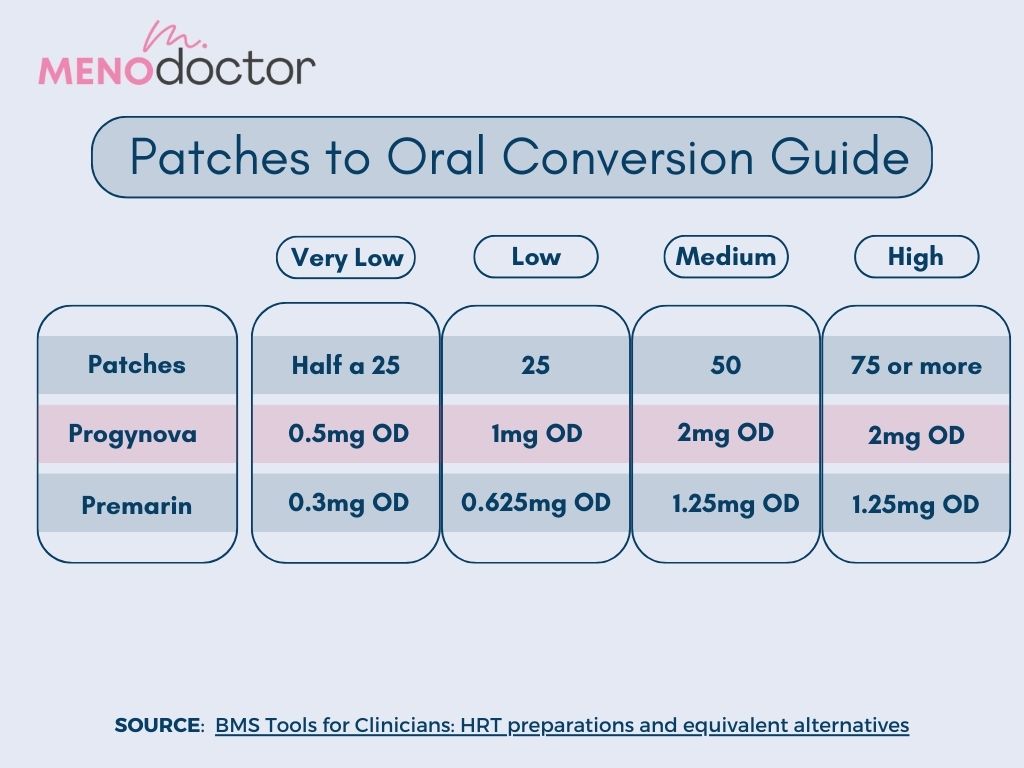
Switching from estradiol patches to tablets requires careful consideration of dosage equivalence. A direct 1:1 conversion isn’t always accurate; you need to consult your doctor for personalized guidance. The bioavailability of estradiol varies significantly between patches and oral tablets.
For example, a 100 mcg estradiol patch might be equivalent to a 1-2 mg oral estradiol tablet, depending on the specific formulation of both the patch and tablet. Several factors influence this, including the type of estradiol used (e.g., estradiol valerate, estradiol hemihydrate), and individual patient factors like metabolism. Your doctor will assess your specific needs and medical history to determine the appropriate tablet dosage.
Don’t attempt self-conversion. Incorrect dosage can lead to hormone imbalances and associated health problems. Regular blood tests are usually recommended during and after the transition period to monitor hormone levels and ensure the chosen dosage is effective and safe for you. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key throughout this process.
Remember: This information is for guidance only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s recommendations for safe and effective hormone replacement therapy.
- Estradiol Patch to Tablet Conversion: Understanding Dosage Equivalents
- Factors Affecting Conversion
- Dosage Ranges & Considerations
- Seeking Professional Guidance
- Calculating Estradiol Dosage: Patch to Tablet Conversion Chart and Considerations
- Practical Guidance for Switching from Estradiol Patches to Tablets: What to Expect
Estradiol Patch to Tablet Conversion: Understanding Dosage Equivalents
Direct conversion between estradiol patches and tablets isn’t straightforward. Bioavailability differs significantly; patches deliver estradiol transdermally, while tablets undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver. Therefore, a simple milligram-to-milligram conversion is inaccurate and potentially harmful.
Factors Affecting Conversion
Several factors influence the equivalent dosage. These include the patch’s formulation (e.g., 0.025 mg/day, 0.05 mg/day, 0.1 mg/day), the brand, the patient’s individual metabolism, and the specific tablet formulation. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Dosage Ranges & Considerations
For example, a 0.05 mg/day estradiol patch might be roughly equivalent to a 1-2 mg oral estradiol tablet daily. However, this is a general estimation and not universally applicable. Your doctor will consider your medical history, symptoms, and response to treatment to determine the appropriate dosage and formulation for you. Regular monitoring of hormone levels is usually necessary. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never attempt self-medication or dosage adjustments based solely on online resources.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Individual needs vary considerably. Only your physician can accurately determine the most suitable estradiol regimen for your unique situation. They will use blood tests and a thorough assessment to make this determination and carefully adjust your treatment as needed.
Calculating Estradiol Dosage: Patch to Tablet Conversion Chart and Considerations
Direct conversion from estradiol patches to tablets isn’t straightforward due to varying formulations and absorption rates. Always consult your doctor for personalized guidance.
However, a general guideline might involve comparing the total daily estradiol delivery. For instance, a 100 mcg/day patch might be roughly equivalent to a 1mg oral tablet taken once daily, or a 0.5mg tablet twice daily, depending on the specific brand and formulation of both the patch and the tablet. This is just an example and not a definitive conversion.
This chart provides a *possible* comparison, but remember this is a simplification and should not be used for self-medication:
| Estradiol Patch (mcg/day) | Approximate Oral Estradiol Tablet Equivalent (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| 25 | 0.25-0.5 |
| 50 | 0.5-1.0 |
| 75 | 0.75-1.5 |
| 100 | 1.0-2.0 |
Factors influencing dosage include your individual metabolism, age, and other health conditions. Blood tests regularly monitor your estradiol levels, ensuring the correct dosage. Your doctor will adjust your medication based on these results. Never adjust your medication without consulting a medical professional.
Oral estradiol tablets typically have a shorter half-life compared to patches, leading to potential fluctuations in blood levels. Patches often provide a more consistent release. Discuss this with your healthcare provider to determine which method better suits your needs.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding your estradiol therapy. They will carefully assess your individual needs and tailor a treatment plan for you.
Practical Guidance for Switching from Estradiol Patches to Tablets: What to Expect
Consult your doctor before making any changes to your hormone replacement therapy. They will help determine the appropriate tablet dosage based on your current patch strength and individual needs.
Expect some fluctuations in your hormone levels during the transition. This is normal. Common side effects include:
- Mild mood swings
- Slight vaginal dryness or discomfort
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
These symptoms usually subside within a few weeks. If they persist or worsen, contact your doctor immediately.
Timing of tablet intake matters. Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding frequency and time of day. Consistency is key for maintaining stable hormone levels.
Pay close attention to any changes in your body and report them to your healthcare provider. This includes unusual bleeding, weight changes, or persistent symptoms.
Your doctor may recommend a gradual transition, starting with a lower tablet dose and gradually increasing it over time. This minimizes the likelihood of experiencing significant side effects.
- Keep a journal to track your symptoms and any changes in your health. This valuable information helps you and your doctor monitor your progress.
- Understand that your experience may differ from others. Each individual responds to hormone therapy uniquely.
- Regular check-ups with your doctor are necessary to monitor hormone levels and adjust the medication as needed.
Remember, open communication with your doctor is paramount throughout this process. They are your best resource for managing the transition and ensuring you receive optimal care.