Need clear information on Sulfasalazine 500mg EC tablets? This guide provides practical details to help you understand this medication. We’ll cover key aspects, including dosage, potential side effects, and important considerations for safe and effective use.
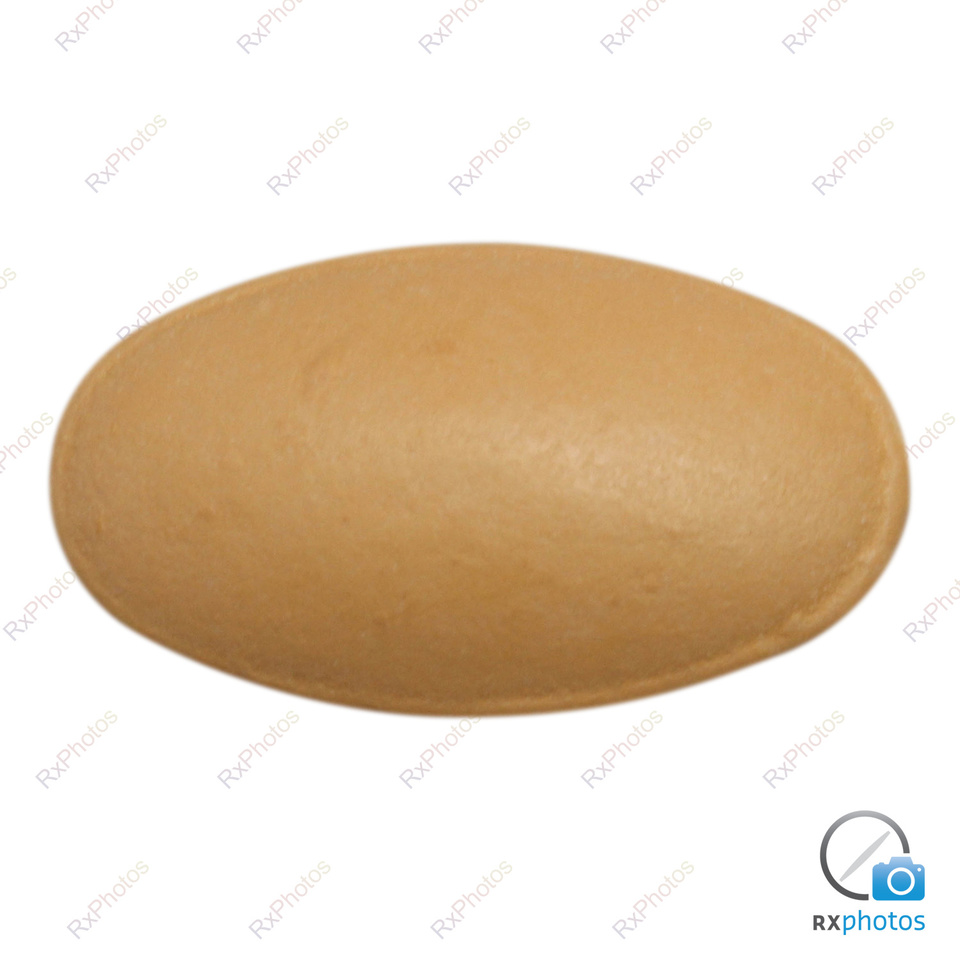
Sulfasalazine 500mg EC tablets are commonly prescribed for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), specifically ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The “EC” signifies enteric-coated, meaning the medication is designed to dissolve in the intestine, not the stomach, minimizing potential stomach upset. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and administration; typical regimens involve taking the tablets twice daily with food.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache. Less frequent but more serious reactions can involve allergic responses and blood disorders. Promptly report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring of blood counts may be recommended, especially during initial treatment. Proper hydration is also crucial for minimizing potential adverse effects. Remember to fully inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, to prevent potential drug interactions.
This information serves as a helpful overview, but it does not replace professional medical advice. Always discuss Sulfasalazine 500mg EC tablets, or any medication, with your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment. They can assess your individual needs and provide personalized guidance.
- Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab: A Detailed Guide
- What is Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab and How Does it Work?
- Common Uses and Conditions Treated with Sulfasalazine
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions Associated with Sulfasalazine
- Drug Interactions and Considerations When Taking Sulfasalazine
- Interactions with Specific Medications
- Additional Factors
- Potential Side Effects Requiring Immediate Attention
- Storage and Disposal of Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab
- Proper Storage Practices
- Safe Disposal
- Important Note
Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Dosage and duration depend entirely on your individual condition and response to treatment.
Sulfasalazine 500mg EC tablets are designed for delayed-release, maximizing absorption in the intestines. This minimizes stomach upset, a common side effect with immediate-release formulations.
- Typical Dosage: Your doctor will determine your specific dosage, which is usually gradually increased. Typical starting doses range from 500mg to 1000mg daily, taken in divided doses.
- Administration: Swallow the tablets whole with a full glass of water. Do not crush, chew, or break the tablets.
- Timing: Take Sulfasalazine with food to further reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
Common side effects include nausea, headache, and diarrhea. Less frequent but more serious effects may include jaundice, allergic reactions, and blood disorders.
- Nausea: Take Sulfasalazine with food to lessen nausea. If nausea persists, consult your physician.
- Diarrhea: Mild diarrhea may resolve on its own. For persistent or severe diarrhea, contact your doctor immediately.
- Serious Side Effects: Seek immediate medical attention for jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), rash, fever, or unusual bleeding or bruising.
Regular blood tests are often recommended to monitor your complete blood count and liver function, especially during initial treatment. This allows your doctor to adjust your dosage or address any potential complications promptly.
- Medication Interactions: Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking, as Sulfasalazine can interact with some drugs, affecting their efficacy or causing adverse effects.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Discuss your treatment plan with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning a pregnancy. Sulfasalazine use during pregnancy and breastfeeding requires careful consideration.
- Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Do not double the dose to make up for a missed one.
Store Sulfasalazine at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep it out of reach of children.
This information is for guidance only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or altering any medication regimen.
What is Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab and How Does it Work?
Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab is an anti-inflammatory medication. It contains sulfasalazine, a drug that works by reducing inflammation in your body. The “EC” stands for enteric-coated, meaning the medication is designed to dissolve in your intestines, not your stomach, minimizing stomach upset.
Sulfasalazine breaks down in the gut into two active components: sulfapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). Sulfapyridine contributes to the overall anti-inflammatory effect, while 5-ASA primarily targets the gut, reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. This dual mechanism makes it effective against certain inflammatory conditions.
Doctors commonly prescribe Sulfasalazine for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. It helps manage symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. It’s also sometimes used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
The medication is typically taken orally, usually twice daily. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Remember, it’s crucial to inform your doctor of any existing medical conditions or medications you are currently taking to prevent potential drug interactions.
Common side effects can include nausea, headache, and abdominal pain. More serious side effects are possible, though less frequent. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience significant side effects, including severe allergic reactions.
Common Uses and Conditions Treated with Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine primarily treats inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).
- Ulcerative colitis: Sulfasalazine helps reduce inflammation and symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding.
- Crohn’s disease: While less effective than in ulcerative colitis, it can manage mild to moderate Crohn’s symptoms.
Beyond IBD, it finds application in other conditions:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It reduces joint inflammation and pain, often used alongside other medications.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Sulfasalazine can help control joint inflammation and skin symptoms associated with this condition.
Specific dosage and treatment duration vary based on the condition and individual response. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Remember, Sulfasalazine can have side effects. Common ones include nausea, vomiting, and headache. Less common but serious side effects are possible. Consult your healthcare provider if you experience any concerning symptoms. They will discuss the benefits and risks associated with Sulfasalazine in your specific case.
- Always inform your doctor about all your medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Sulfasalazine.
- Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Follow prescribed dosage meticulously. Do not adjust the dosage without consulting your doctor.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab
Begin with a low dose and gradually increase it as tolerated. A typical starting dose is one 500mg tablet twice daily with food. This helps minimize stomach upset.
Adjustments depend on individual response and the specific condition being treated. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. Closely follow their instructions.
Always swallow the tablets whole; do not chew or crush them. This ensures proper absorption and reduces the risk of side effects.
Take the medication at evenly spaced intervals throughout the day. For example, if you take two tablets daily, consider taking one in the morning and one in the evening.
Consistent medication intake is vital for optimal results. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
| Typical Starting Dose | One 500mg tablet twice daily |
|---|---|
| Administration | Swallow whole with food |
| Dosage Adjustments | Based on individual response; follow your doctor’s instructions |
| Missed Dose | Take as soon as remembered, unless it’s near the next dose. Do not double up. |
Report any side effects to your doctor immediately. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and headache. Serious side effects are less frequent but require prompt medical attention.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions Associated with Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine can cause various side effects, some common and others less frequent. Common side effects include nausea, headache, and loss of appetite. These typically lessen as your body adjusts to the medication. Less common, but still possible, side effects are abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Serious, though rare, side effects include allergic reactions such as rash, itching, or swelling. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention. Blood disorders are another potential, though infrequent, risk. Regular blood tests may be recommended, especially during the initial treatment period, to monitor for any abnormalities.
Sulfasalazine may affect liver function. Your doctor might order liver function tests to monitor this aspect. Additionally, the drug may reduce the effectiveness of some vaccines, so inform your healthcare provider about all vaccinations before and during treatment. It’s also crucial to be aware that sulfasalazine can impact folic acid absorption, potentially leading to deficiency. Your doctor may recommend folic acid supplementation.
Before starting sulfasalazine, inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. This helps prevent potential drug interactions. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are significant considerations. Discuss these with your doctor before starting or continuing sulfasalazine use as it may not be appropriate in these situations. Finally, monitor yourself for any unusual changes in your health and promptly consult your doctor if you have concerns.
Drug Interactions and Considerations When Taking Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine interacts with several medications. Avoid taking it with folic acid supplements, as sulfasalazine can interfere with folic acid absorption; your doctor may prescribe a higher dose of folic acid to counteract this. Concurrent use with methotrexate may increase the risk of methotrexate toxicity, requiring close monitoring.
Interactions with Specific Medications
Antidiabetic medications: Sulfasalazine may increase the effect of insulin or oral hypoglycemics, potentially leading to hypoglycemia. Monitor your blood sugar levels carefully if you take both. Digoxin: Sulfasalazine can reduce digoxin absorption, affecting its therapeutic level. Regular blood tests to check digoxin levels are crucial. Warfarin: Sulfasalazine can enhance the effect of warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. Close monitoring of your INR (International Normalized Ratio) is necessary.
Additional Factors
Sulfasalazine can cause photosensitivity, increasing your sun sensitivity. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when exposed to sunlight. It can also affect kidney and liver function, so regular blood tests to monitor these functions are recommended. Inform your doctor about any allergies to sulfa drugs before starting sulfasalazine. Pregnancy and breastfeeding also influence its use; discuss these aspects with your healthcare provider before taking this medication.
Potential Side Effects Requiring Immediate Attention
Serious allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, demand immediate medical attention. Also, seek medical help immediately if you experience severe abdominal pain, bloody stools, or signs of liver damage (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Storage and Disposal of Sulfasalazine 500mg EC Tab
Store Sulfasalazine 500mg EC tablets at room temperature, between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C). Keep the bottle tightly closed to protect from moisture.
Proper Storage Practices
Avoid extreme temperatures, direct sunlight, and excessive humidity. These conditions can degrade the medication, reducing its effectiveness. Always check the expiration date on the bottle before using the medication. Dispose of expired Sulfasalazine properly.
Safe Disposal
Never flush medication down the toilet or pour it into a drain. Instead, follow these steps: Mix the tablets with an undesirable substance, like used coffee grounds or kitty litter. Seal the mixture in a sturdy plastic bag and place it in your household trash. This prevents accidental ingestion or environmental contamination. Contact your local pharmacy or waste disposal service for specific guidance on medication disposal in your area if needed. They can provide further details on appropriate disposal methods.
Important Note
Consult your pharmacist or doctor for any questions regarding storage or disposal of your medication. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.